Understanding VPNs: What They Are, How They Work, and Choosing the Best VPN for Your Needs
Questions of privacy and security are very significant in this digital living age. You might be browsing, streaming your favorite content, or even working remotely; you would definitely want to save your online activities from prying eyes. This is where a Virtual Private Network (VPN) comes into play. VPNs are powerful tools designed to enhance your security while browsing online and to protect your privacy, hence opening up access to everything that is restricted in your region. In this article, we will look at precisely what a VPN is, how it works, what types of VPNs are available, and what their benefits and drawbacks are. We will contrast paid-for and free VPN services and try to help you make a decision as to which one to opt for about your usage.

What Is a VPN?
A virtual private network allows you to create a secure connection over the internet to another network. VPNs hide your IP address, shield your online activity from prying eyes, and encrypt all the data transferred between the server and your device; things internet service providers, hackers, advertisers, and other third parties are looking to peek at.
This is simply elaborated on by means that when one connects using a VPN onto the internet, it uses a front secure server in between, which the VPN provider usually owns. It might be located in another country and not only provides the service of privacy protection but also gives assistance in skipping any geographic restrictions on some content, like streaming services or websites blocked in your area.
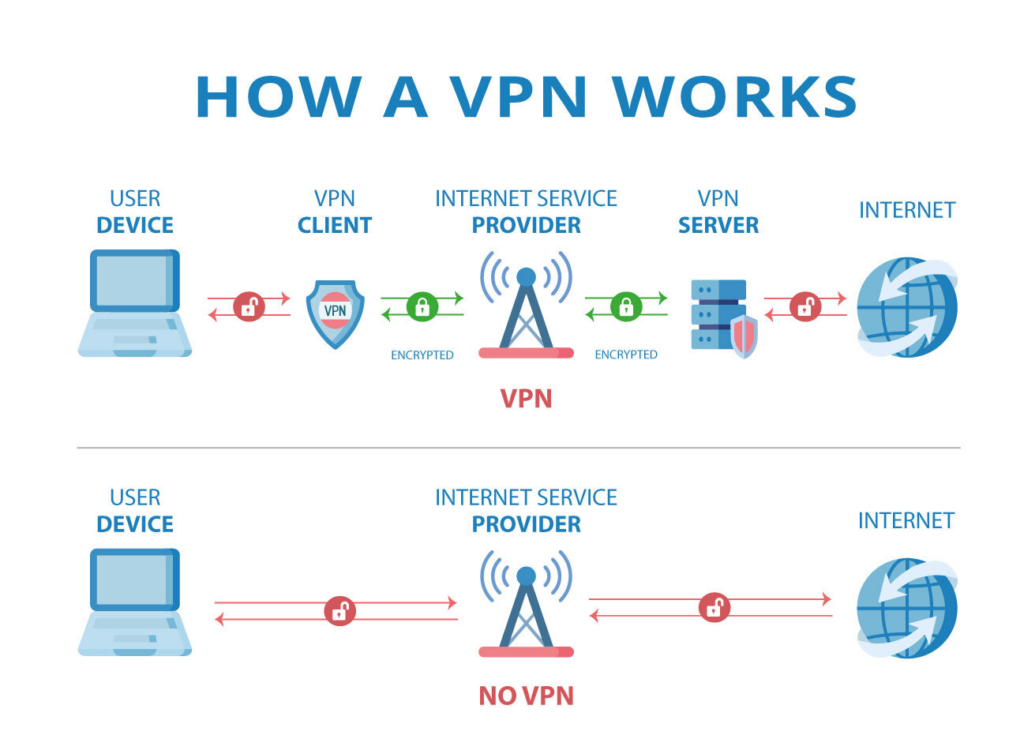
How does a VPN work?
A secure tunnel is opened between the user’s device and the Internet. The step-by-step details of the whole process are explained below.
1. Encryption:
When a user is connected to a VPN, all the internet traffic gets encrypted. This in essence means that when data is sent back from a user’s device, it will be jumbled into some unreadable format. Only a VPN server can decrypt the data.
2. IP Address Masking:
The ISP assigns your device a unique identifier known as an IP address. After logging in to a VPN, it will conceal the actual IP address with that of the VPN server. In effect, this masks location and then appears as if you are browsing from somewhere else.
3. Secure Connection:
The VPN will tunnel a secure connection between your device and the VPN company’s server. This connection is what people refer to as a “tunnel” because it hides your data from anyone sniffing around in your online activities. This in turn is very vital when using the open, public Wi-Fi hotspots that are of lesser security.
4. Get Access to Restricted Content from Anywhere:
A VPN really does make the whole process of getting access to restricted content around the globe easier by hiding your IP address. Say, by using a VPN, you will go with an IP address set from another region to unblock streaming services like Netflix, Hulu, or BBC iPlayer in order to view a wide range of content.
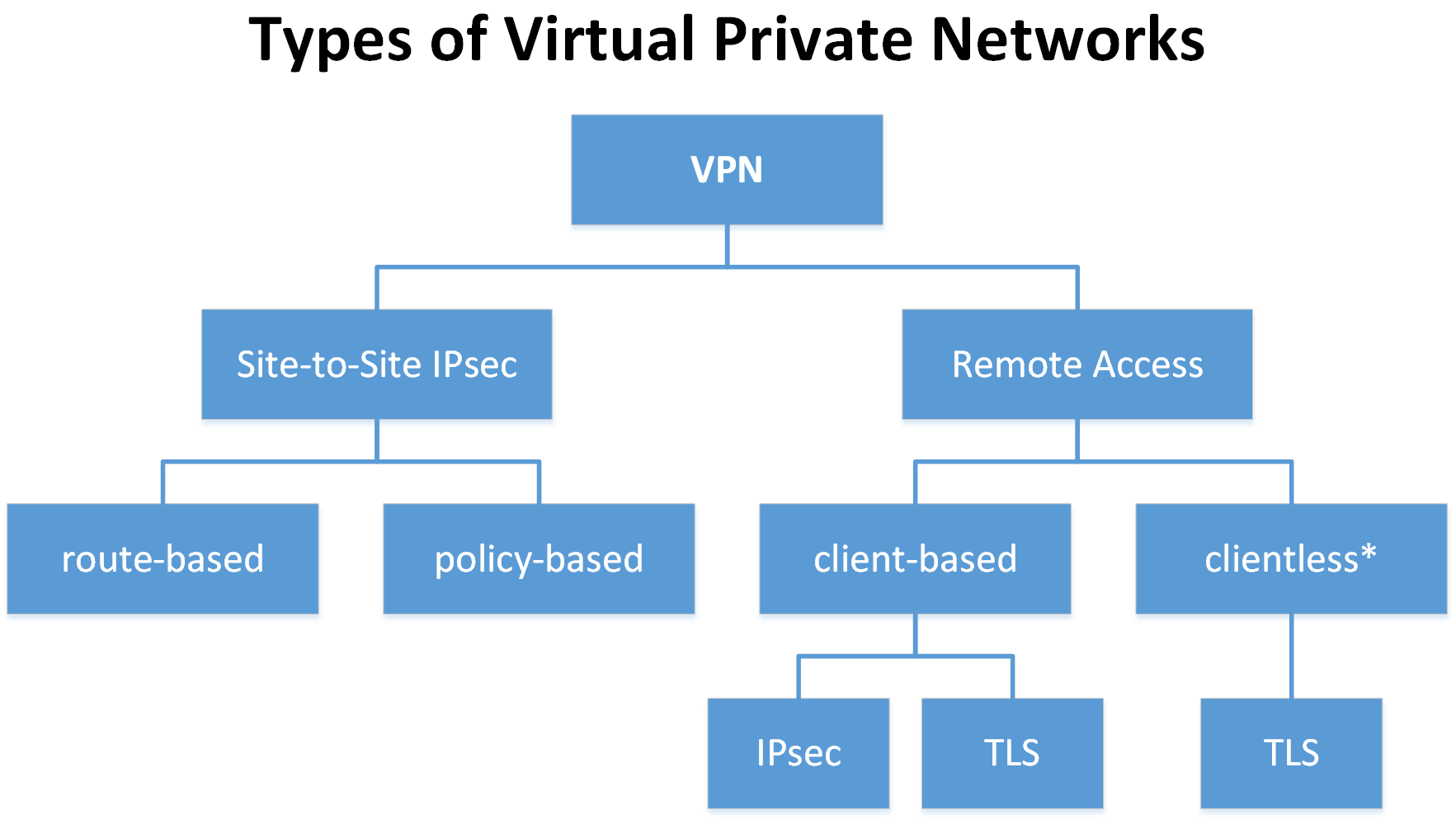
Types of VPNs
Many types of VPNs serve different purposes. Knowing them will enable you to choose which one will work for you best.
1. Remote Access VPN:
It is the most typical type of VPN used by individual users. It allows a user to connect to a private network from a different location, normally when working from home. Usually, remote access VPNs are utilized to secure the internet connection and safeguard data while surfing.
2. Site-to-Site VPN:
This one is also known as a router-to-router VPN. Businesses largely use this kind of VPN in order to connect various office network locations. In the site-to-site VPN, the resources can be shared and communication can be done safely by the workers working from different offices as if they were working from the same local network.
3. Client-Based VPN:
This involves installing a VPN client on your device. It is a solution largely employed by private users who seek an easy-to-use VPN solution. Using the client, establish a secure connection to the VPN Server, which both encrypts your data and masks your IP address.
4. SSL VPN:
Secure Sockets Layer VPNs are primarily used for access to specific applications or services, rather than to a full network. They are usually accessed via a web browser and find broad applications in corporate environments where, for example, employees need access to some particular tools remotely.
5. IPSEC VPN:
They are connections fathomed towards securing internet communications based on IP networks. They find a quite good number of applications in site-to-site VPNs and provide a higher order of security during the transmission of data.

Pros and Cons of VPNs
Like any other technology, VPNs also have their pros and cons. Knowing these will let you decide on the basis of your needs whether a VPN is right for you or not.
Pros:
Better Privacy: Because it conceals your IP address, due to the encryption of data, tracking gets very hard to do. This comes in handy with respect to guarding privacy from ISPs, ads, government surveillance, etc.
Wi-Fi Security: Everyone knows public Wi-Fi is insecure, making it the first target of hackers. Thus, a VPN ensures that data is secure and safe by encrypting the connection so that even with insecure Wi-Fi areas, your information is still private.
Bypass Geographical Restrictions: VPNs give access to content that is limited in your country. The streaming services, websites, online services—regional restrictions are all bypassed and more diverse content is available over the network.
Anonymity: In this way, it conceals your real IP address, hence allowing you a good level of anonymity that might save you from identity theft, focused advertisement, and internet tracking.
Cons:
Decreased Speed: Naturally, the speed will be reduced as your data is being encrypted and relayed through another VPN server. This slowing helps you notice well in the free VPNs with limited server capacity.
Chance of a Decreased Reach: Some websites even end up blocking traffic from known IP addresses that belong to popular VPN servers. That means you won’t be able to reach certain content even with a VPN.
Price: Most good VPN services are available only at a cost of subscription. There may be services of free price, but in most cases, they turn out to have slow speeds, fewer server locations, and limited usage data.

Paid vs. Free VPN:
What’s in the Difference?
Now, every time one wants to subscribe to a VPN, he has to consider whether he wants to subscribe to a free or a paid-for VPN. Of course, each has merits that go with the different trade-offs between the two.
Paid VPNs:
Almost every paid VPN comes with helpful and powerful features in order to provide the best possible user experience. These usually include higher connection speeds, more servers available in various locations, unlimited data usage, and advanced security features such as a kill switch. Most paid VPNs are scored to be much more secure and reliable than free ones.
Free VPNs:
While they definitely are very alluring, there are big limitations that most free VPNs come with. Free VPNs usually have restricted server choices, speed, and data caps. Some free VPNs log your data or flash ads to generate revenues at the cost of your privacy. But if you are only going to need a VPN infrequently, or if you are under such an incredibly tight budget that free is what you can afford, you may find that free VPNs are sufficient.
Free VPNs: Pros and Cons
Pros:
Free: This pretty much explains itself. One of the obvious advantages of free VPN services is that they do not charge subscribers in any form. This definitely gives it great appeal to those who require basic VPN capabilities and would not like to pay for a subscription.
Easy to use: Most of the free VPNs are pretty straightforward; thus, they are easily usable. Usually, they have user-friendly interfaces and fast setup steps.
Cons:
Limited Features: Most free VPNs have reduced functionality compared to the paid alternatives. This simply means they have fewer server locations, slow speed, and limited data usage. These limitations may affect the overall performance and usability of the VPN.
Privacy Concerns: Some free VPN providers log data or have ad displays that leak out your privacy. Any use of free VPN requires one to choose a credible service provider who will not do these activities.
Unreliable Performance: Seeing as the vast majority of free VPN servers have low capacity, and most people are reaching out to use them, they generally amount to slow speeds and really bad connections. This can be very frustrating if you wanted to stream content or do anything that would require a stable connection.
Free VPNs: Advantages vs. Disadvantages
Advantages:
Free: The most obvious benefit of free VPN is that it’s free. This makes it very attractive for those who need basic VPN and do not subscribe.
User-friendly: Most free VPNs are relatively user-friendly, hence they offer a good option for those who aren’t tech-savvy. In most cases, they have simple interfaces with easy setup procedures.
Disadvantages:
Limited Features: Most free VPNs have reduced functionality compared to their paid counterpart. This comes in the form of fewer locations available for servers, slower speed, and a limited amount of data usage. All these things can hit at the performance and usability of the VPN.
privacy Concerns: Some free VPNs log users’ data or even display ads that leak your privacy. One major factor of consideration when using a free VPN would be that the Service Provider upholds the standards.
Unreliable Performance: Most free VPNs are really slow because of the low capacity of their servers, compared to high demand. Moreover, you will often experience your connection as the worst during very busy server times, which becomes frustrating especially when streaming content or trying to do something that requires a stable connection.
Choosing the Right VPN for Your Needs
Choose your VPN based on what you want to do and how each type can do it. Say you want a VPN that’s the best for everyday use; you can opt for the paid services from ExpressVPN, NordVPN, or CyberGhost. These give you rapid speeds, huge location ranges, and nice safety features. If you are really strapped for cash, some of the best free VPN options would be ProtonVPN, Windscribe, and TunnelBear. All three offer basic VPN services at decent performance.
It would, therefore, suit a person whose prime interest is the ease of use to have a VPN with an intuitive interface and fast setup methods. Most of the high-ranking VPN providers provide user-friendly applications where connecting to a server requires just two or three clicks. Furthermore, if your number one priority is privacy, look for a VPN with a no-logs policy that is absolute, accompanied by state-of-the-art complementary security features such as a kill switch and DNS leak protection.
Conclusion
If you do care about your online privacy and security, a VPN is the most important tool in your armor. Be it protecting your data on public Wi-Fi, accessing restricted content, or just browsing the web anonymously—a VPN has your back. While choosing a VPN, remember to consider the difference between paid and free services and their respective pros and cons. Understanding how a VPN works and what exactly one is looking for in a service, one can make a choice of the best VPN suitable for everyday use that allows protection of privacy and access to worldwide content.

Leave a Reply