Understanding VPNs: The Difference Between VPN and Group VPN
In today’s world, the prime focus is on privacy and security concerns within the digital domain. VPNs turned out to be handy tools for protecting sensitive data while retaining information privately for individuals and businesses alike while being online. Since the number of VPNs available is big, most people hardly know which one best suits their needs. The blog covers the differences between VPN and Group VPN, the advantages, and disadvantages of each of them, and various types of VPNs and their uses.

What is a VPN?
Virtual Private Network service that provides a secure encrypted connection between your device and the internet. In other words, it could be said to provide some sort of “tunnel” when your device reaches the Internet, enabling you to keep your online activities private from hackers, surveillance by the government, or even other curious individuals who may have bad intentions for your data.
Uses of VPN
Privacy Protection: VPNs are going to mask your IP address; thereby, it becomes very difficult for any website and third parties to trace your online activities.
Access to Restricted Content: With the use of VPNs, one may access different Geo-restricted and censored content that may not be available in your region.
Secure Remote Access: Many organizations and companies also make use of VPNs to securely connect their employees to the company’s networks while working remotely from other locations.
Public Wi-Fi Safely: VPNs encrypt your data against everyone whenever you use Wi-Fi hotspots, which are by nature less secure than others and usually become targets for cyber-attacks.
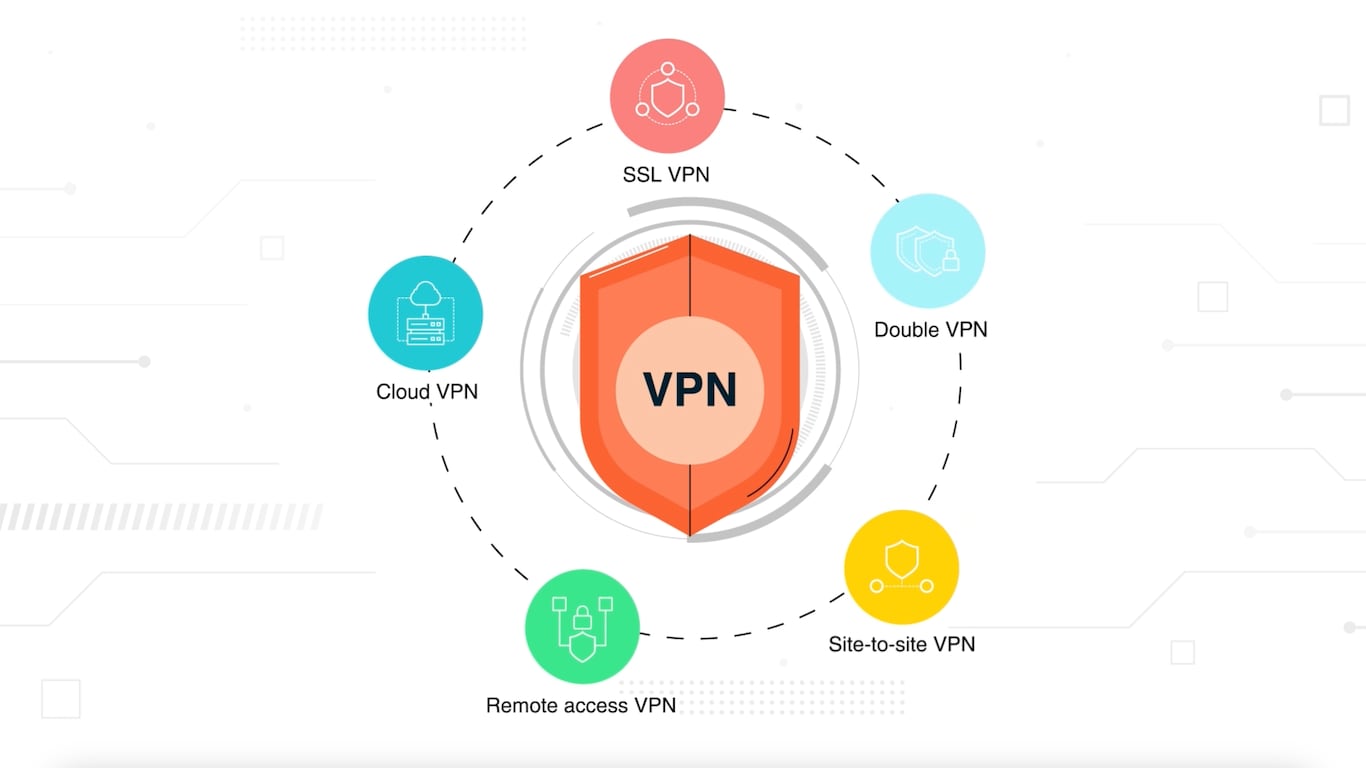
Different Types of VPNs
1. Remote Access VPN
A Remote Access VPN performs the function of allowing users to connect to any private network from any part of the globe. This mode of VPN is being increasingly utilized by lots of people and businesses, in general, to connect securely to their home or office network from anywhere across the globe. It is ideal for remote workers who need to access the company’s resources securely.
Pros: Very easy to implement and use; access can be securely obtained from anywhere in the world to a private network.
Cons: Can be slower due to encryption overhead; may require additional software.
2. Site-to-Site VPN
Among all methods, Site-to-Site VPNs are one of the most adopted ways for enterprise businesses to establish connectivity among other different networks at different locations. It enables building a secure connection between two or more sites, such as head offices and branch offices of other organizations, in a way that they could share resources and communicate as if they were on the same local network.
Pros: Suitable for the connection of many sites that enhance communications as well as the sharing of different resources.
Cons: Somewhat complex regarding its establishment, as it requires similar hardware and software configuration at each site.
3. SSL VPN
An SSL VPN is based on the SSL protocol in the establishment of a secure connection between a user device and a VPN server. It finds its application mostly in the case of remote access. It can also be accessed through a web browser, with no requirement for dedicated VPN software.
Pros: Very easy to operate; additional software is not required; secure connections can be provided using web browsers.
Cons: Limited to certain applications, full network access is not always allowed.
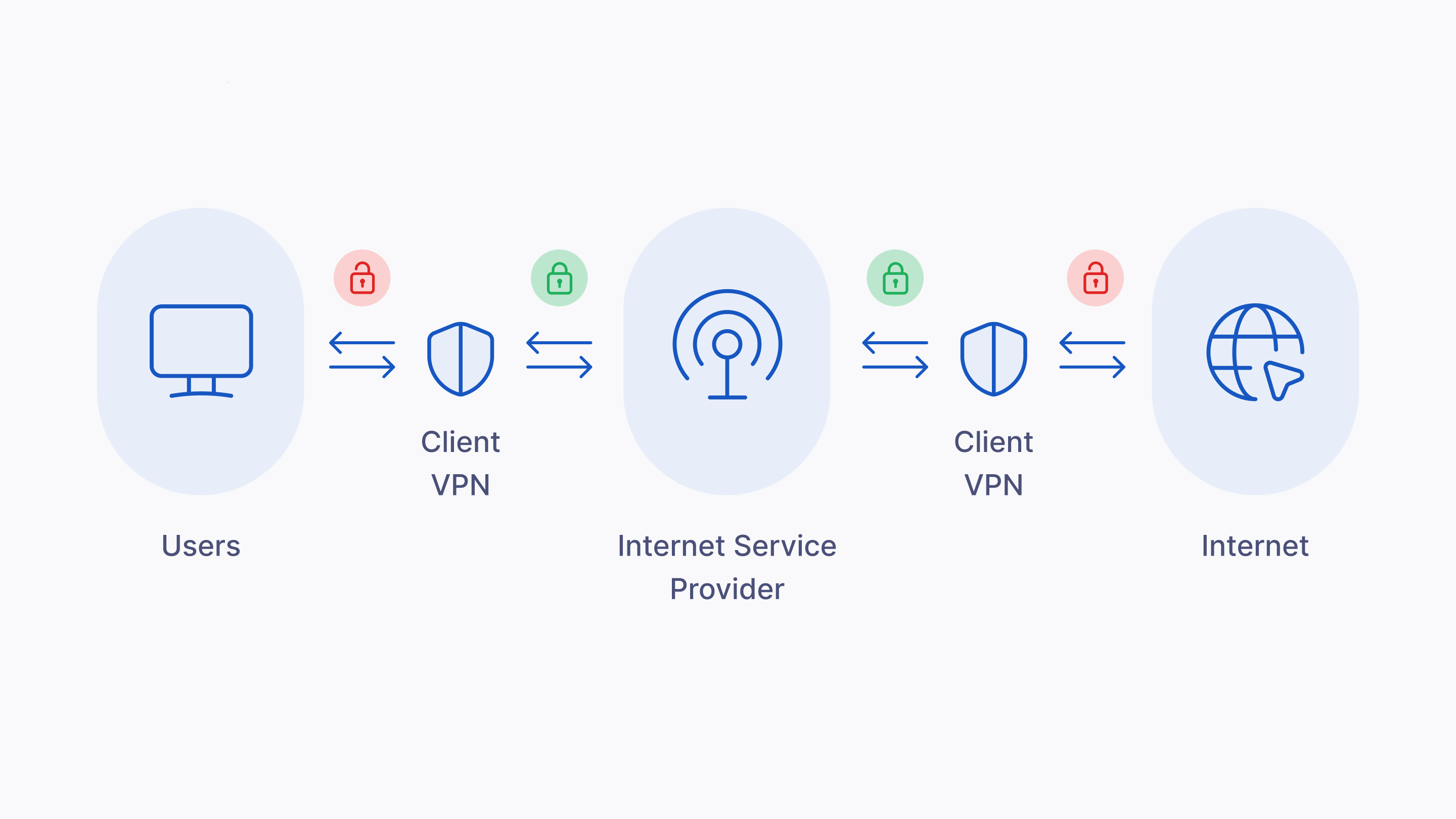
4. Client-to-Server VPN
A Client-to-Server VPN is one in which individual users, accessing using a remote access VPN, connect to a central server. These are utilized by organizations to enable employees to securely connect to the company’s internal network.
Pros: The management is centralized; allows home and other remote employees to securely access.
Cons: The server periodically needs maintenance; there is a potential for bottlenecks if many users log in at the same time.
5. Group VPN
This variety of VPN allows a group of users, under a defined group, to connect using only one VPN connection. This would be particularly useful in organizational settings where several employees or members want secure access to the same resources.
Pros: Effective for the organization as it saves several subscriptions; ease of management of VPNs for groups; and enables security in collaboration.
Cons: There is a potential for lower performance when too many users share one connection; it requires very attentive management to be secure.
Differences Between VPN and Group VPN
1. Individual vs. Group Access
VPN: Basically, they have been designed for individual use, creating a secure connection for one user to a private network or to the internet. Each user is required to establish a separate VPN connection.
Group VPN: This involves many users within a group, and it allows sharing of a single VPN connection. It becomes handy in organizations that want to provide security to a group of employees or members.
2. Management and Scalability
VPN: It is simpler to administer a VPN at the level of individual users, though as it scales up in use for multiple users within an organization, it could be very complex and more expensive because each would have to be connected individually.
Group VPN: As far as the use by organizations is concerned, group VPN is much more scalable since multiple users can now be joined using only a single VPN setup. Controlling user access and securing the group is difficult in this, which does not work out without proper planning.
3. Performance and Security
VPN: The performance level for individual users is quite the same, as each user enjoys a unique connection. Security is less challenging to manage since each user has a different tunnel that is encrypted.
Group VPN: Performance may become poor due to the sharing of many users through the same connection, that is, it slows down once the connections become heavy. Security management, it might be more complex, especially when more users access the same VPN, the tendency to have it breached is high if not managed properly.
Pros and Cons of VPN and Group VPN
VPN
Pros:
1. Excellent individual privacy and security
2. Consistent performance for single users
3. Easier to deploy personally
Cons:
1. Expensive and complicated to deploy in multiple users
2. Each user has to manage his VPN himself
3. Less Scalable for organizations
Group VPN
Pros:
1. Economical for organizations having more than one user
2. Simplifies the management of Group VPN
3. Allow sharing of resources and collaboration securely
Cons:
1. Performance may degrade if the number of users is high
2. More challenging process of security management
3. A single point of failure may impact the entire group
How to Choose the Right VPN According to Your Needs
Ultimately, choosing the right VPN is a question of needs. If you want to keep privacy and security as an individual for personal use, you’ll want to stick with a standard service. If you’ve got the responsibility of taking care of an army of end users or an organization, Group VPN offers scaling and management tools that let you secure several users efficiently.
Conclusion
Your needs and the scale of use will define which one should be chosen: a VPN or Group VPN. A VPN would be perfect for an individual or even a small business, where strong privacy and secure connections are needed at an individual level. If your organization is huge or you have a team, the Group VPN scales up pretty well in a very cost-effective manner that allows multiple users to securely access shared resources. Both are amazing ways to protect your online activities, and data privacy, and permit safe network access. Their differences and uses can only be well comprehended by knowing how to make an appropriate choice of VPN, which can fit into meeting one’s goal either at the personal level or for organizational security.

Leave a Reply